All light is composed of photons: small packets of light energy in the form of waves with a defined frequency and wavelength. However, not all light is the same. Different wavelengths of light represent different colors on the light spectrum. When light is projected as a single, coherent wavelength where the waves travel parallel to each other, it’s considered laser light.
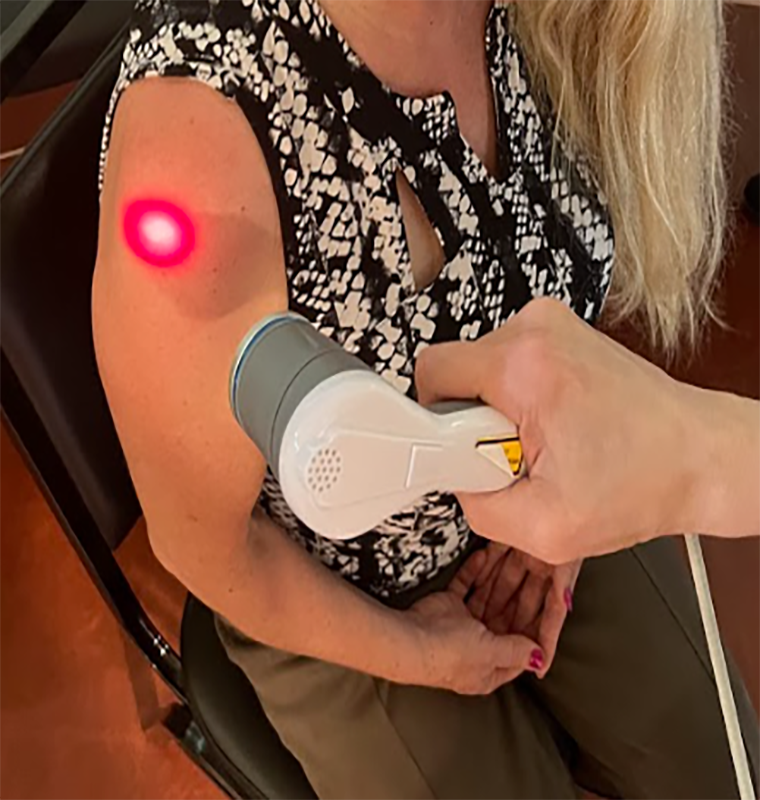
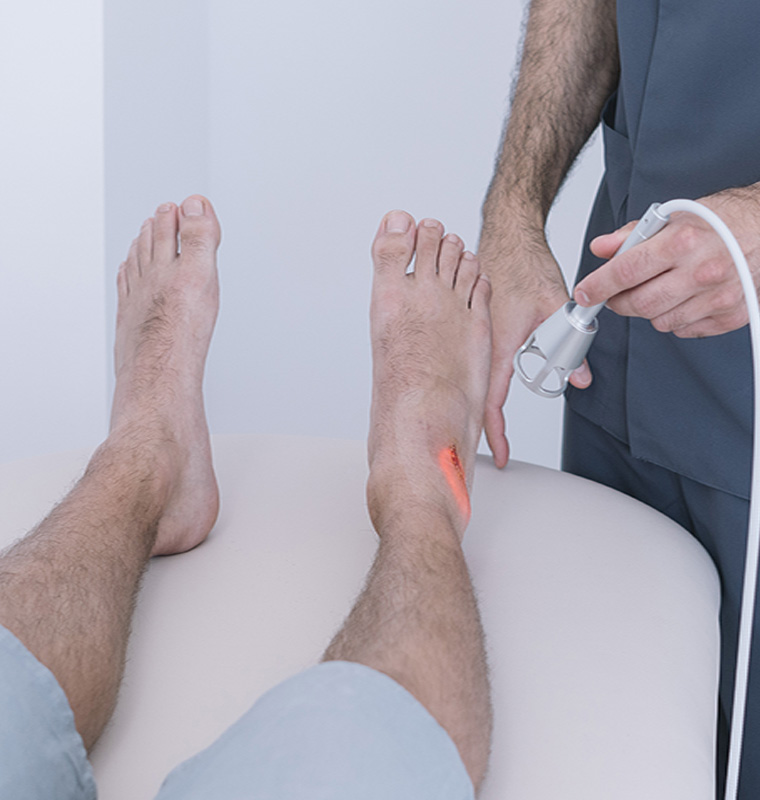
Laser light is much more intense than regular white light and has a multitude of applications from scanning barcodes to treating pain, inflammation, and more within human (and animal) bodies.Laser therapy is when laser light is tuned to specific wavelengths and frequencies and applied to an organism in order to stimulate metabolic processes at the cellular level.Laser light holds its intensity until it is absorbed by a medium; in the case of laser therapy, the medium is the body.
The photon energy of laser light can effectively penetrate the skin and underlying structures, which accelerates the body’s natural healing process. Laser therapy utilizes the wavelengths and frequencies of visible red and near infrared (NIR) light to treat a variety of conditions at their source within the body through safe, non-invasive, and painless procedures.
Photochemical Action
Studies have shown that when tissue cultures are irradiated by lasers, enzymes within cells absorb energy from laser light. Visible red light and near infrared (NIR) are absorbed within the mitochondria and the cell membrane. This produces higher ATP levels and boosts DNA production, leading to an increase in cellular health and energy.
Therefore, when applied as treatment, lasers have been shown to reduce pain and inflammation as well as stimulate nerve regeneration, muscle relaxation, and immune system response. Lasers have no effect on normal tissues because photons of light are only absorbed and utilized by the cells that need them.
Role of Chromophores
Chromophores are components of various cells and subcellular organelles which absorb light. The stimulation of chromophores on mitochondrial membranes incites the production of ATP.
This results in:
- Increased cellular energy levels
- Pain relief
- Accelerated cellular healing